
Bitcoin faucets are online platforms or apps that reward users with small amounts of Bitcoin, called satoshis, in exchange for completing simple tasks. These tasks could be as straightforward as solving captchas, clicking ads, or filling out surveys. The term “faucet” comes from the idea of a dripping tap, offering small yet consistent amounts of Bitcoin over time.
Purpose and Significance
Bitcoin faucets play an essential role in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. They were created to spread awareness and adoption of Bitcoin by making it accessible to everyone, especially beginners. Here’s why they matter:
- Introduction to Bitcoin
- Faucets serve as entry points for newcomers to explore Bitcoin without financial risk. By completing tasks and earning small amounts of cryptocurrency, users learn about wallet creation, transactions, and blockchain technology.
- Promoting Microtransactions
- Faucets demonstrate the power of Bitcoin for microtransactions, showcasing its ability to handle low-value transfers efficiently. This highlights Bitcoin’s versatility beyond investment and trading.
- Educational Value
- They teach users how to interact with cryptocurrencies in a hands-on way—key concepts like private key management and blockchain confirmations are introduced through real-world applications.
- Driving Decentralisation
- Faucets align with the decentralised ethos of cryptocurrencies. They make Bitcoin distribution more inclusive, ensuring anyone can own a small piece of the digital asset, no matter their financial background.
- Gateway to Broader Ecosystem
- Many Bitcoin faucet platforms integrate with other blockchain tools, like decentralised applications (dApps) and Lightning Network payments, offering users a glimpse into the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
For a comprehensive look at how Bitcoin faucets contribute to accessibility and education, don’t miss Benefits of Bitcoin Faucets: Promoting Accessibility and Adoption. This article dives deeper into the multifaceted advantages of faucets, from driving decentralization to showcasing microtransactions.
Key Things to Know
- Origins: The first Bitcoin faucet, created by Gavin Andresen in 2010, gave away 5 BTC per user to promote adoption.
- Tiny Payouts: Satoshis earned via faucets are often small, but over time, they add up.
- Revenue Model: Faucets generate income through ads and sponsorships, redistributing a portion to users.
- Accessibility: Faucets are free to use and require no upfront investment, making them a low-risk starting point for crypto exploration.
- Educational Tool: They simplify complex cryptocurrency concepts, making Bitcoin more approachable for newcomers.
Bitcoin faucets are more than just free Bitcoin providers—they’re an accessible, educational gateway to the world of cryptocurrency. Their continued relevance highlights the importance of onboarding users into decentralised finance.
What Are Bitcoin Faucets?
Definition
Bitcoin faucets are websites or apps that give out small amounts of Bitcoin, called satoshis, as rewards for completing simple tasks. These tasks might include:
- Solving captchas
- Watching advertisements
- Clicking on links
- Answering surveys
- Playing games
The rewards are micro-payments, designed to be accessible even for users who are completely new to Bitcoin.
How Do They Work?
- Users sign up and provide a Bitcoin wallet address.
- They complete small tasks to earn satoshis (fractions of Bitcoin).
- Earnings are stored in a micro wallet until they reach a minimum withdrawal limit.
- Once the limit is hit, users can transfer their Bitcoin to a main wallet.
The process highlights Bitcoin’s ability to handle microtransactions while giving users hands-on experience with the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Origin of Bitcoin Faucets
Bitcoin faucets started as a way to promote adoption and education.
In 2010, Gavin Andresen, one of Bitcoin’s earliest developers, created the first-ever Bitcoin faucet.
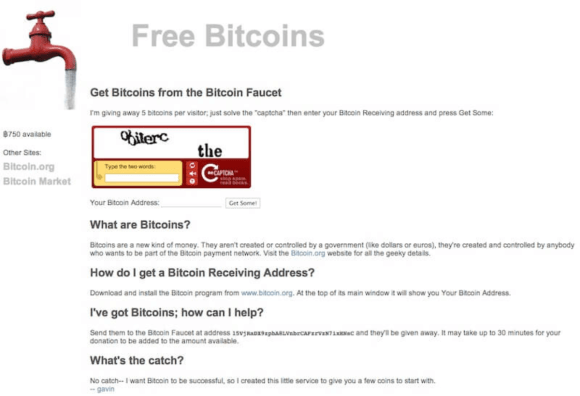
- It gave away 5 BTC per user—worth just pennies at the time.
- The goal was to introduce people to Bitcoin by letting them experience transactions without buying Bitcoin first.
- Andresen’s faucet distributed 19,700 BTC in total before running out of funds.
That’s now worth millions of dollars—a testament to Bitcoin’s growth since its early days.
Historical Context and Impact
Bitcoin faucets were crucial in:
- Spreading awareness when Bitcoin was largely unknown.
- Demonstrating utility by showing how Bitcoin transactions work.
- Building trust in cryptocurrency by allowing people to test it for free.
Today, faucets serve a similar role, especially as entry points for newcomers exploring Bitcoin and decentralised finance.
For a broader overview of the origins, mechanisms, and impact of Bitcoin faucets, read Bitcoin Faucet Explained—How It Works and Why It Matters.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin faucets distribute free Bitcoin to promote adoption and education.
- The first faucet by Gavin Andresen gave away 5 BTC per user—a staggering amount in today’s terms.
- Faucets remain relevant tools for learning about Bitcoin, microtransactions, and blockchain technology.
How Do Bitcoin Faucets Operate?
Bitcoin faucets run on a simple process designed to reward users with small amounts of Bitcoin, called satoshis, for completing basic online tasks.
User Registration Process
To get started, users typically:
- Sign Up: Register on the faucet platform with an email address.
- Provide a Bitcoin Wallet Address: Users enter a wallet address where rewards will eventually be sent.
- Create a Micro Wallet (Optional): Many faucets require a micro wallet to collect small payouts until they reach a minimum withdrawal amount.
- Verification (if needed): Some platforms use email confirmation or CAPTCHA tests to prevent bots.
No upfront payments are required, making faucets low-risk and highly accessible.
Types of Tasks Required
Earning Bitcoin from faucets involves completing quick, low-effort tasks, such as:
- Solving CAPTCHAs: Prove you’re human by identifying letters, numbers, or images.
- Clicking Ads: View ads and interact with promotional content.
- Watching Videos: Short advertisements or tutorials related to crypto.
- Answering Surveys: Provide feedback or opinions in exchange for rewards.
- Playing Games: Mobile or web-based games that integrate faucet rewards.
- Refer-a-Friend Programs: Earn commissions by referring new users.
Each task generates revenue for faucet operators through advertising fees, affiliate programs, or sponsorships, allowing them to share a portion of profits with users.
Reward System: Earning Satoshis
- What Are Satoshis?
- A satoshi is the smallest Bitcoin unit, equal to 0.00000001 BTC.
- How Are Rewards Calculated?
- Most faucets distribute 10–100 satoshis per task, depending on the task’s difficulty and time required.
- Timers and Frequency:
- Users may need to wait for a cooldown timer (e.g., 5 minutes) before claiming the next reward.
- Some faucets offer hourly spins or bonus rewards for consecutive visits.
Role of Micro Wallets in Managing Payouts
Micro wallets are essential tools for faucet users because they:
- Handle Small Transactions: Store tiny Bitcoin amounts without incurring large blockchain fees.
- Aggregate Earnings: Collect rewards from multiple faucets in one place until the total reaches the payout threshold.
- Automate Withdrawals: Transfer funds to a full Bitcoin wallet once the balance hits a set minimum (e.g., 10,000 satoshis).
Example Micro Wallet Providers:
- FaucetPay – Popular for collecting faucet earnings.
- CoinPot – Previously used for micro-payouts before closing in 2021.
- ExpressCrypto – Supports multiple cryptocurrencies in addition to Bitcoin.
Micro wallets make faucets sustainable by solving the problem of high transaction fees for microtransactions.
Key Takeaways
- Users register, complete simple tasks, and earn satoshis as rewards.
- Tasks range from captchas and ads to games and surveys.
- Rewards are collected in micro wallets to minimise fees and simplify withdrawals.
- The faucet model is scalable and remains an effective way to introduce users to Bitcoin transactions and blockchain technology.
Economic Model Behind Bitcoin Faucets
Bitcoin faucets operate on a simple but effective revenue model that balances earning opportunities for users with profitability for operators. The system is fueled by advertising revenue, affiliate programs, and sponsorships, ensuring faucet platforms remain financially sustainable despite distributing free Bitcoin.
Revenue Generation for Faucet Operators
Bitcoin faucets don’t give away free cryptocurrency out of generosity. Instead, they generate revenue through:
- Advertising Revenue:
- Faucets display ads from Google AdSense, media networks, and crypto ad platforms.
- Users need to click ads, watch videos, or view pop-ups, which generates income for the faucet owner.
- Example: High-traffic faucets can earn $1–$10 per 1,000 ad views depending on ad type.
- Affiliate Marketing:
- Users are encouraged to invite others using referral links.
- Faucets often pay 10–50% commissions on the earnings of referred users.
- This creates viral growth, driving traffic and more ad revenue.
- Sponsorship Deals:
- Some faucets partner with crypto wallets, exchanges, or mining platforms that pay for exposure.
- Sponsored content and ads target crypto-curious users visiting these platforms.
- Premium Features:
- Some faucets upsell additional services, like faster withdrawals or higher payouts, generating income directly from users.
Distribution of Earnings to Users
Faucet operators redistribute a portion of their earnings to users in the form of satoshis (fractions of Bitcoin). Here’s how it works:
- Task Completion: Users perform actions like clicking ads or solving CAPTCHAs to earn points converted into satoshis.
- Timers and Claim Limits: Faucets often impose a cooldown timer (e.g., 5–15 minutes) between claims to reduce overuse.
- Daily Limits and Bonuses: Users may receive loyalty rewards or bonuses for visiting regularly.
- Payout Thresholds: Earnings are stored in micro wallets until users accumulate enough satoshis for withdrawal.
Example Earnings Range:
- 100–200 satoshis per claim on average.
- High-paying faucets can offer up to 1,000 satoshis per claim during promotions.
- Based on data from Coinmetro, faucet users can earn roughly $0.50–$3 per day, depending on activity.
Sustainability Challenges
While faucets were highly profitable in Bitcoin’s early days, sustainability has become a challenge as cryptocurrency values increased.
- Lower Rewards Due to Rising Bitcoin Prices:
- Bitcoin’s value surged, making even small satoshis more expensive to give away.
- Operators had to lower payouts to avoid losses, reducing user interest.
- Ad Revenue Dependency:
- Revenue fluctuates with advertising rates and traffic volume.
- Ad blockers further reduce click-based income, impacting faucet profitability.
- Fraud and Abuse:
- Bots and multiple account fraud drain funds, forcing operators to introduce CAPTCHA systems and anti-spam tools.
- Fraud prevention increases operational costs, cutting into profits.
- Transaction Fees and Withdrawals:
- High Bitcoin transaction fees make micro-payments inefficient.
- Faucets rely on micro wallets to group payouts, but fees still rise during network congestion.
Key Takeaways
- Faucets earn money through ads, affiliates, and sponsorships while sharing a fraction of earnings with users.
- Micro wallets play a critical role in managing payouts, reducing transaction costs.
- Rising Bitcoin prices and fraudulent activity make faucet operations less profitable over time.
- New technologies like the Lightning Network could help faucets process payments more efficiently in the future.
Technological Infrastructure of Bitcoin Faucets
Bitcoin faucets rely on efficient payment systems to handle microtransactions, ensuring users can claim small rewards without being affected by high transaction fees. The backbone of this infrastructure includes micro wallets and the Lightning Network, which streamline payments and make the faucet model sustainable.
Micro Wallets: Managing Small Payments
Micro wallets are specialised wallets designed to aggregate small payments before transferring them to a user’s primary Bitcoin wallet.
How They Work:
- Collection Point: Micro wallets store multiple small transactions (satoshis) earned from faucets.
- Threshold Limits: Users must reach a minimum balance (e.g., 10,000 satoshis) before transferring funds to their main wallet.
- Low Transaction Fees: By batching withdrawals, micro wallets reduce the impact of blockchain fees, making tiny payouts viable.
Popular Micro Wallet Providers:
- FaucetPay: Supports multiple cryptocurrencies and enables quick payouts.
- ExpressCrypto: Previously popular, though it ceased operations in 2022.
- CoinPot: Offered combined balances but closed in 2021, reflecting the evolving landscape.
Benefits of Micro Wallets:
- Efficiency: Prevents paying high transaction fees for small transfers.
- Consolidation: Combines earnings from multiple faucets into one balance.
- Automation: Simplifies withdrawals once thresholds are met.
Challenges with Micro Wallets:
- Centralised Control: Some services require trust in third-party operators, reducing decentralisation.
- Platform Shutdowns: Users risk losing funds if providers shut down without notice.
The Lightning Network: Boosting Microtransactions
The Lightning Network is a second-layer solution built on Bitcoin’s blockchain. It enables faster and cheaper transactions—a game-changer for faucets and micro-payments.
How It Works:
- Creates off-chain payment channels between parties, allowing near-instant Bitcoin transfers.
- Only the opening and closing transactions are recorded on the blockchain, reducing fees.
Benefits for Bitcoin Faucets:
- Lower Costs: Transactions are processed off-chain, cutting fees to fractions of a cent.
- Speed: Payments clear instantly, unlike regular Bitcoin transactions that can take 10–60 minutes for confirmation.
- Scalability: Handles thousands of transactions per second, making it ideal for high-volume platforms like faucets.
- Micropayment Support: Makes it profitable to send and receive tiny payments, overcoming Bitcoin’s earlier limitations.
Real-World Impact:
- Faucets adopting the Lightning Network can now offer instant payouts, removing withdrawal delays.
- Users avoid network congestion during periods of high blockchain activity, ensuring smooth earnings transfers.
Example Lightning Network Faucets:
- Bitrefill Faucet: Offers Bitcoin micropayments directly through Lightning.
- ZEBEDEE: Provides rewards for in-game Bitcoin earnings, leveraging Lightning’s instant transactions.
Key Takeaways
- Micro wallets streamline Bitcoin faucets by bundling small payments, reducing fees and improving withdrawal efficiency.
- The Lightning Network allows fast, low-cost microtransactions, making faucets scalable even in periods of high Bitcoin adoption.
- Combined, these technologies modernise the faucet model, ensuring it remains relevant and profitable despite challenges like rising fees and network congestion.
Educational and Adoption Benefits of Bitcoin Faucets
Bitcoin faucets do more than just hand out free satoshis—they act as learning tools that introduce new users to the cryptocurrency world. By offering a risk-free entry point, faucets lower the barriers to understanding Bitcoin, blockchain technology, and digital payments.
Introducing New Users to Bitcoin
Bitcoin faucets serve as stepping stones for beginners who are curious about cryptocurrency but hesitant to invest their own money.
Key Benefits for New Users:
- Risk-Free Exploration: Faucets provide small amounts of Bitcoin at no cost, allowing users to experiment without financial commitment.
- Hands-On Experience: Users actively interact with wallets, transactions, and private keys, gaining practical knowledge.
- Simplified Onboarding: Faucets break down complex cryptocurrency concepts into simple steps, making Bitcoin accessible to everyone.
Real-World Example:
Early faucets, such as Gavin Andresen’s first Bitcoin faucet, distributed 5 BTC per user in 2010 to boost adoption when Bitcoin was still unknown. This model proved effective, leading to wider public awareness of cryptocurrencies.
Teaching Wallet Creation and Transaction Processing
Bitcoin faucets walk users through critical processes like:
- Creating a Wallet: Users set up either a micro wallet or a main wallet to store their earnings. This teaches them the importance of:
- Private keys for security.
- Seed phrases for backup and recovery.
- Understanding Transactions: Faucets allow users to:
- Track transactions on the blockchain using block explorers.
- Learn how confirmations and fees impact payments.
- Manage microtransactions effectively through batch payments.
- Handling Withdrawals: Users experience real-time withdrawals, learning how to send and receive Bitcoin safely.
This step-by-step learning experience prepares users for more advanced interactions with cryptocurrency exchanges and decentralised finance (DeFi) platforms.
Contribution to Broader Cryptocurrency Adoption
Faucets do more than educate individuals—they play a key role in growing the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Key Contributions:
- Building Trust in Blockchain Technology: Faucets offer proof-of-concept demonstrations of how Bitcoin works, building confidence in its reliability.
- Promoting Decentralisation: Users learn about Bitcoin’s role in eliminating intermediaries and enabling peer-to-peer payments.
- Encouraging Participation in Crypto Markets: After gaining initial exposure through faucets, many users go on to buy, trade, and invest in cryptocurrencies.
- Driving Innovation in Micropayments: Faucets highlight Bitcoin’s potential for handling microtransactions, paving the way for gaming rewards, loyalty programs, and dApp integrations.
Case Study:
According to a report by CoinDesk, faucets have played a role in onboarding millions of users into Bitcoin, especially in countries with limited access to traditional financial systems.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin faucets provide a hands-on introduction to cryptocurrency for beginners.
- Users learn about wallet creation, transactions, and security in a practical environment.
- Faucets act as entry points into the larger crypto world, encouraging participation and investment.
- They help promote mass adoption by breaking down barriers to entry and offering risk-free exposure.
Case Studies and Statistics on Bitcoin Faucets
Bitcoin faucets have evolved significantly since their inception, offering insights into user engagement, payout structures, and the broader adoption of cryptocurrency. Below are key case studies and statistics that shed light on how faucets have operated over the years and their current state in 2024.
Average Payouts in 2024
Modern Bitcoin Faucets:
- In 2024, the average faucet pays users a few cents to a couple of dollars per hour, depending on platform traffic and the value of Bitcoin.
- Low-Reward Faucets: Users typically earn 100–200 satoshis per task (equivalent to $0.02–$0.05 per task at a Bitcoin price of $25,000).
- High-Reward Faucets: Some faucets offer bonus spins or referral incentives, pushing earnings closer to $1–$3 per hour for highly active users.
Factors Affecting Earnings:
- Bitcoin Price Volatility: Rising Bitcoin prices reduce the amount of satoshis distributed.
- Task Complexity: Faucets requiring surveys or app downloads may offer higher payouts.
- Traffic Volume: Platforms with more users often dilute individual rewards to maintain sustainability.
- Historical Impact: Early Faucets Distributing Whole Bitcoins
The First Bitcoin Faucet (2010):
- Created by Gavin Andresen, the first faucet distributed 5 BTC per user to encourage Bitcoin adoption.
- At the time, Bitcoin’s value was less than $1, so the giveaways seemed insignificant.
Impact:
- Over its lifetime, the faucet gave away 19,700 BTC, valued at over $500 million today.
- It introduced thousands of users to Bitcoin, many of whom became long-term crypto enthusiasts or investors.
Other Early Faucets:
- During Bitcoin’s early years (2010–2013), many faucets offered 0.1–1 BTC per claim, as transaction fees were negligible.
- These faucets played a key role in onboarding users who later helped drive Bitcoin’s adoption.
Evolution of User Engagement Over Time
Bitcoin faucets have transformed significantly to adapt to technological and market changes:
2010–2013: The Generous Era
- High payouts (whole Bitcoins) were common due to low transaction fees and Bitcoin’s minimal market value.
- Engagement was driven by curiosity about this new digital currency.
2014–2018: Consolidation and Popularity
- Faucets started focusing on ads and affiliate programs for revenue.
- Payouts shifted to fractions of Bitcoin, reflecting rising market value.
- Platforms introduced gamification elements like bonus spins and loyalty rewards to retain users.
2019–2024: Scalability and Adaptation
- Adoption of micro wallets and the Lightning Network to handle payouts efficiently.
- Lower payouts due to Bitcoin’s rising value but increased focus on user engagement through surveys, games, and referrals.
- Faucets diversified, offering multi-crypto payouts to attract a broader audience.
Key Takeaways
- Earnings Today: Users earn between $0.50–$3 per hour depending on activity level and platform.
- Historical Generosity: Early faucets like Gavin Andresen’s distributed entire Bitcoins, playing a pivotal role in Bitcoin’s adoption.
- Evolving Engagement: Faucets have shifted from simple giveaways to more interactive platforms using gamification and ad-based models.
Bitcoin faucets remain relevant as educational tools and onboarding platforms for cryptocurrency, though their economic model has adapted to changing times.
Challenges and Criticisms of Bitcoin Faucets
While Bitcoin faucets have played a significant role in promoting cryptocurrency adoption, they face several challenges that affect their long-term sustainability. From fraud and abuse to declining rewards and user experience issues, faucets must constantly adapt to remain viable.
Fraud and Abuse (Bots and Exploits)
One of the biggest challenges for Bitcoin faucets is fraudulent activity, including:
- Bot Attacks:
- Automated programs are often used to repeatedly claim rewards, draining faucet funds quickly and unfairly.
- Impact:
- Operators lose revenue and legitimate users receive lower payouts.
- Multiple Accounts (Sybil Attacks):
- Users create multiple identities to bypass claim limits and cooldown timers.
- CAPTCHA Solvers:
- Fraudsters use automated tools to solve captchas, making it harder for faucets to identify genuine users.
- IP Address Manipulation:
- Proxy servers and VPNs are used to bypass IP restrictions, allowing repeated claims.
Countermeasures:
- Most faucets now require email verification, CAPTCHAs, and IP tracking to prevent abuse.
- Advanced platforms leverage machine learning algorithms to detect suspicious activity.
Despite these efforts, fraud prevention increases operational costs, impacting faucet profitability.
Declining Rewards Due to Rising Bitcoin Value
Bitcoin’s value has skyrocketed since faucets were first introduced. In 2010, 5 BTC giveaways were worth less than $1. Today, 5 BTC is worth over $200,000, making such payouts unsustainable.
Impact on Earnings:
- Most faucets now pay only 100–200 satoshis per claim (about $0.02–$0.05), leaving users frustrated with low rewards.
- Users need to spend hours clicking ads or completing tasks to earn even $1–$3 per day.
- Faucets have had to reduce payouts further during Bitcoin bull runs, as maintaining high rewards became impossible.
Key Stats (2024):
- Average faucet earnings: $0.50–$3 per hour based on activity level.
- Minimum withdrawal thresholds: 10,000–50,000 satoshis, which may take weeks to achieve depending on payouts.
Solutions Being Tested:
- Integrating the Lightning Network to reduce transaction fees, enabling faster and cheaper payouts.
- Exploring multi-crypto faucets offering tokens like Dogecoin and Litecoin, which are more affordable for microtransactions.
User Experience Concerns
Many faucets have shifted their focus toward ads and affiliate programs, sometimes at the expense of user experience.
Common Complaints:
- Intrusive Ads:
- Pop-ups, redirects, and auto-play videos frustrate users and create a spammy experience.
- Lengthy Payout Processes:
- Users often have to wait weeks or months to reach the minimum payout amount.
- Hidden Fees:
- Some faucets charge withdrawal fees, further reducing actual earnings.
- Trust Issues:
- Many faucets shut down unexpectedly, leaving users unable to withdraw funds.
- Users are often sceptical of new faucets due to scams and rug pulls.
Improvements Needed:
- Better user interface designs to simplify navigation.
- Transparent payout systems to build trust.
- Improved mobile compatibility, as more users access faucets via smartphones.
Key Takeaways
- Fraud and Abuse: Bots, VPNs, and CAPTCHA solvers make faucet management expensive and complex.
- Lower Rewards: Rising Bitcoin values have drastically reduced payouts, limiting user earnings.
- Poor User Experience: Ad-heavy platforms and long payout delays lead to user dissatisfaction.
Future Outlook:
Bitcoin faucets need to evolve by:
- Leveraging technologies like the Lightning Network to reduce costs.
- Offering multi-crypto rewards to sustain higher payouts.
- Improving security systems to block fraudulent activity and enhancing user experiences for better retention.
Future Prospects of Bitcoin Faucets
Bitcoin faucets continue to evolve as technology advances and cryptocurrency adoption grows. While traditional faucet models face challenges, new opportunities have emerged through decentralised applications (dApps), blockchain innovations, and layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network. These advancements are helping faucets stay relevant in the ever-changing crypto landscape.
Adaptation to New Technologies and Platforms
Bitcoin faucets are embracing modern technologies to improve efficiency and user experience:
- Lightning Network Integration:
- Faucets are adopting the Lightning Network to handle instant micropayments with lower fees.
- This allows faucets to offer faster withdrawals and higher payouts, addressing one of their biggest challenges—transaction costs.
- Mobile and Web3 Applications:
- Faucets are moving to mobile-friendly platforms and integrating with Web3 wallets to simplify access.
- Example: Some faucets now allow users to connect their MetaMask wallets or scan QR codes for payments, enabling a seamless experience.
- Faucets are moving to mobile-friendly platforms and integrating with Web3 wallets to simplify access.
- Gamification and Rewards Systems:
- Modern faucets incorporate games, quizzes, and challenges to keep users engaged.
- Platforms like ZEBEDEE even offer Bitcoin rewards for in-game actions, blurring the line between gaming and earning.
- Multi-Crypto Support:
- Many faucets now distribute multiple cryptocurrencies, catering to the growing interest in altcoins and tokenised assets like Ethereum and Dogecoin.
Integration with Decentralised Applications (dApps)
Decentralised applications (dApps) offer exciting opportunities for Bitcoin faucets to grow beyond their current use cases:
- Smart Contract Faucets:
- Faucets can be built directly on Ethereum, Polygon, or other blockchain networks using smart contracts to automate payouts and improve transparency.
- dApp Partnerships:
- Faucets can integrate with DeFi platforms and NFT marketplaces, allowing users to earn Bitcoin rewards while interacting with decentralised finance tools or purchasing NFTs.
- Token Rewards and Staking Incentives:
- Faucets may evolve to include staking programs, where users lock up cryptocurrency to earn additional rewards, combining faucets with yield farming concepts.
- Micropayment Infrastructure for dApps:
- Faucets could power microtransactions within dApps, enabling payments for content, services, or gaming rewards without traditional payment systems.
Ongoing Relevance in the Cryptocurrency Landscape
Despite challenges, Bitcoin faucets remain relevant as:
- Educational Tools:
- Faucets continue to provide hands-on training for new users, teaching them about wallets, transactions, and blockchain security.
- Low-Risk Entry Points:
- Faucets allow curious users to experiment with cryptocurrencies without the risk of losing money.
- Marketing Channels:
- Cryptocurrency companies use faucets as advertising platforms to promote their products, services, and tokens.
- Scaling Opportunities with Layer-2 Solutions:
- Technologies like the Lightning Network make faucets more sustainable by reducing fees and speeding up payments, keeping faucets practical even with small payouts.
- Web3 and Metaverse Integration:
- Faucets could be integrated into metaverse platforms, offering users rewards for virtual activities, enhancing engagement in virtual economies.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin faucets are adapting to modern technologies like the Lightning Network and Web3 wallets to improve scalability and efficiency.
- Integrations with decentralised applications (dApps) could expand their functionality, merging them with DeFi tools and gaming platforms.
- Faucets remain relevant by acting as educational tools, marketing platforms, and gateways to broader cryptocurrency adoption.
- As the crypto ecosystem evolves, faucets will likely become part of larger decentralised infrastructures, enabling microtransactions and rewards systems in the digital economy.
Conclusion: The Role and Impact of Bitcoin Faucets
Bitcoin faucets have played a pivotal role in introducing millions of people to the cryptocurrency world. Starting as simple giveaways of whole Bitcoins in 2010, faucets have evolved into interactive platforms that educate users, promote blockchain adoption, and demonstrate the potential of microtransactions.
They’ve proven to be:
- Educational Tools: Teaching users about wallets, transactions, and blockchain security without financial risks.
- Onboarding Platforms: Lowering barriers to entry for newcomers, making cryptocurrency more accessible.
- Marketing Channels: Offering businesses a way to reach crypto-savvy audiences through ads and referrals.
- Proof-of-Concept Systems: Highlighting Bitcoin’s ability to handle micropayments efficiently.
Final Thoughts on Their Significance in the Digital Economy
Bitcoin faucets continue to adapt as cryptocurrency technologies advance. With innovations like the Lightning Network and Web3 integrations, faucets remain relevant tools for educating users and enabling low-cost transactions.
Looking ahead:
- Faucets are likely to become part of decentralised applications (dApps) and gaming ecosystems, offering rewards through blockchain-powered platforms.
- They will maintain their role as entry points for crypto adoption, providing low-risk learning environments for beginners.
- As digital economies expand, faucets could support micropayment systems and tokenised incentives, reinforcing Bitcoin’s value beyond speculation and trading.
While individual faucet platforms may come and go, the core concept of using microtransactions to engage users and promote adoption will continue to influence the cryptocurrency ecosystem.